Main Applications of Ozone
―Water treatment―
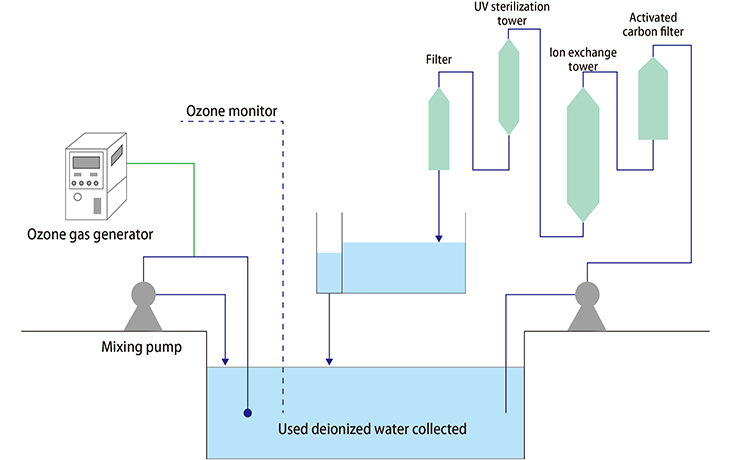
Deionized water recovery (sterilization and recycling of deionized water)
- Effect of ozone
- Extending the life of filters and ion exchange resin through ozone sterilization of used deionized water
See details of products: FX Series , NZR Series
Sterilization
- Effect of ozone
- Reducing power consumption by utilizing ozone sterilization as an alternative to thermal sterilization
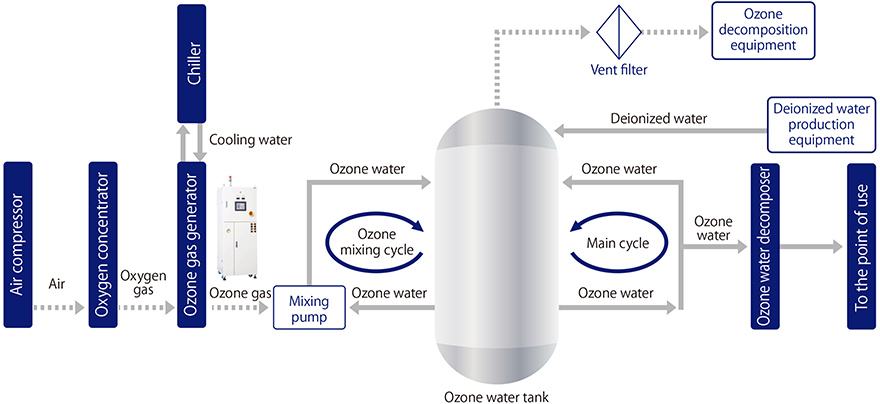
<Outline of ozone sterilization process>
- Ozone is made to come in contact with raw water at all times during the ozone mixing cycle to maintain dissolved ozone concentration at a certain level.
- Dissolved ozone is decomposed by the ozone water decomposer when supplying sterilized water to the point of use.
<Advantages of the use of ozone>
- (1) Safe and pollution-free
- While sodium hypochlorite and other chemicals have the risk of staying behind after use for sterilization and causing other problems, ozone is self-decomposed and therefore does not cause such problems.
- (2) Reduced duration of line stop
- When hot water is used for sterilization, lines have to be stopped. However, because ozone water is circulated at all times in our systems, there is no need to stop lines for sterilization.
- (3) Improved safety management and quality
- Ozone concentration is monitored and maintained at a certain level at all times, allowing you to indirectly monitor the status of sterilization.
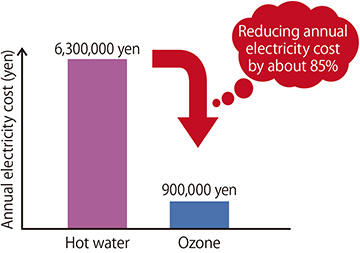
<Cost comparison between hot water sterilization and ozone sterilization>
Conditions: water treatment capacity: 20 tons; heatup time from 20 to 80˚C: 60 min.
■ Hot water sterilization
1,400 kw × 15 yen/kwh × 300 days/year = 6,300,000 yen/year
■ Sterilization using an ozone system
200 kw × 15 yen/kwh × 300 days/year = 900,000 yen/year
*Calculated based on electric capacity of an ozone generator, oxygen concentrator, mixing pump, chiller, and compressor of a 20-ton ozone system
See details of products: FX Series
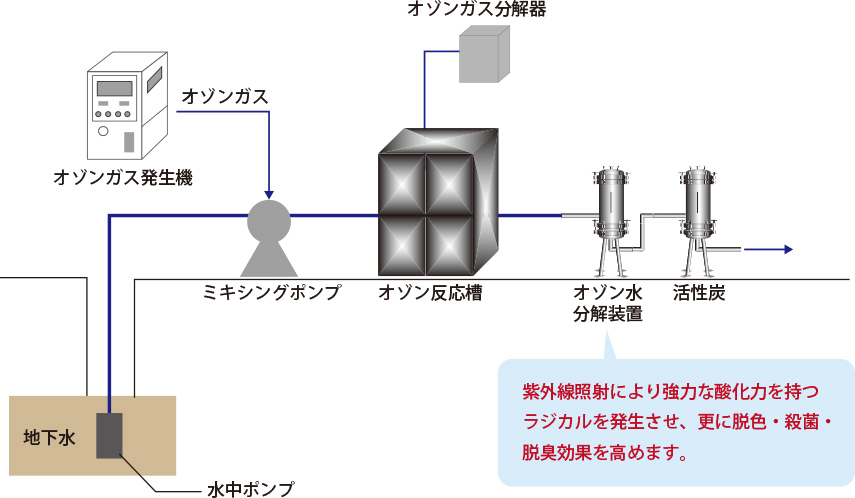
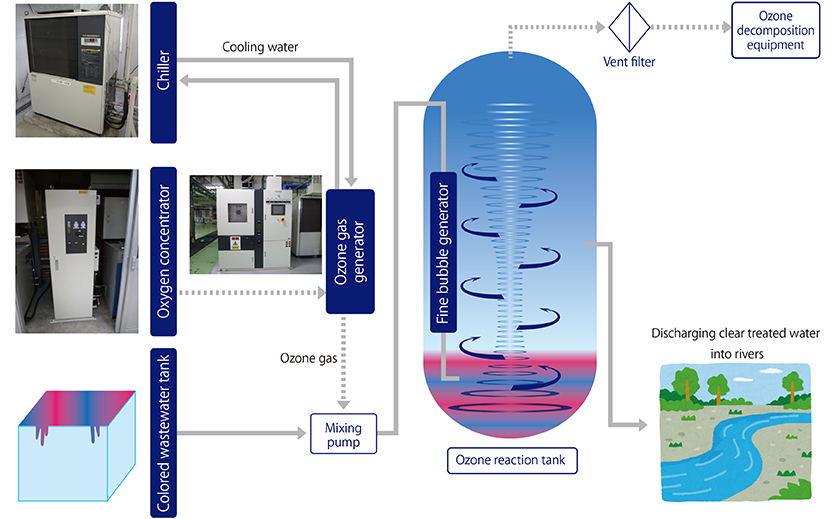
Groundwater treatment
- Effect of ozone
-
- Decolorization (decomposition of humic substances), increased clearness
*The opposite effect—colorization of water—may result depending on the water quality due to oxidation of iron, etc. - Sterilization (Legionella, coliform, mold virus)
- Deodorization
- Extension of the life of activated carbon at the rear stage
- Decolorization (decomposition of humic substances), increased clearness